Nitrogenous Bases In Dna
QUICK AND EASY Overview of hydrolysis and dehydration synthesis. Nitrogenous bases pair together in the following way.

Nitrogenous Base Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock

Nucleosides Vs Nucleotides Purines Vs Pyrimidines Nitrogenous Bases Dna Rna Youtube
Nitrogenous Bases And Dna Emma Benjaminson Mechanical Engineering Graduate Student
The backbone of A-DNA is formed by sugar phosphates that are linked continuous using phosphodiester bonds.

Nitrogenous bases in dna. Two sugar-phosphate chains are paired through hydrogen bonds between A and T and between G and C thus forming the twin-stranded double helix of the DNA molecule. A phosphate group a sugar group and one of four types of nitrogen bases. Nitrogenous bases present in the DNA can be grouped into two categories.
Nucleobases also known as nitrogenous bases or often simply bases are nitrogen-containing biological compounds that form nucleosides which in turn are components of nucleotides with all of these monomers constituting the basic building blocks of nucleic acidsThe ability of nucleobases to form base pairs and to stack one upon another leads directly to long-chain helical structures such. DNA is usually a double-stranded polymer of nucleotides although single-stranded DNA is also known. DNA is made of chemical building blocks called nucleotides.
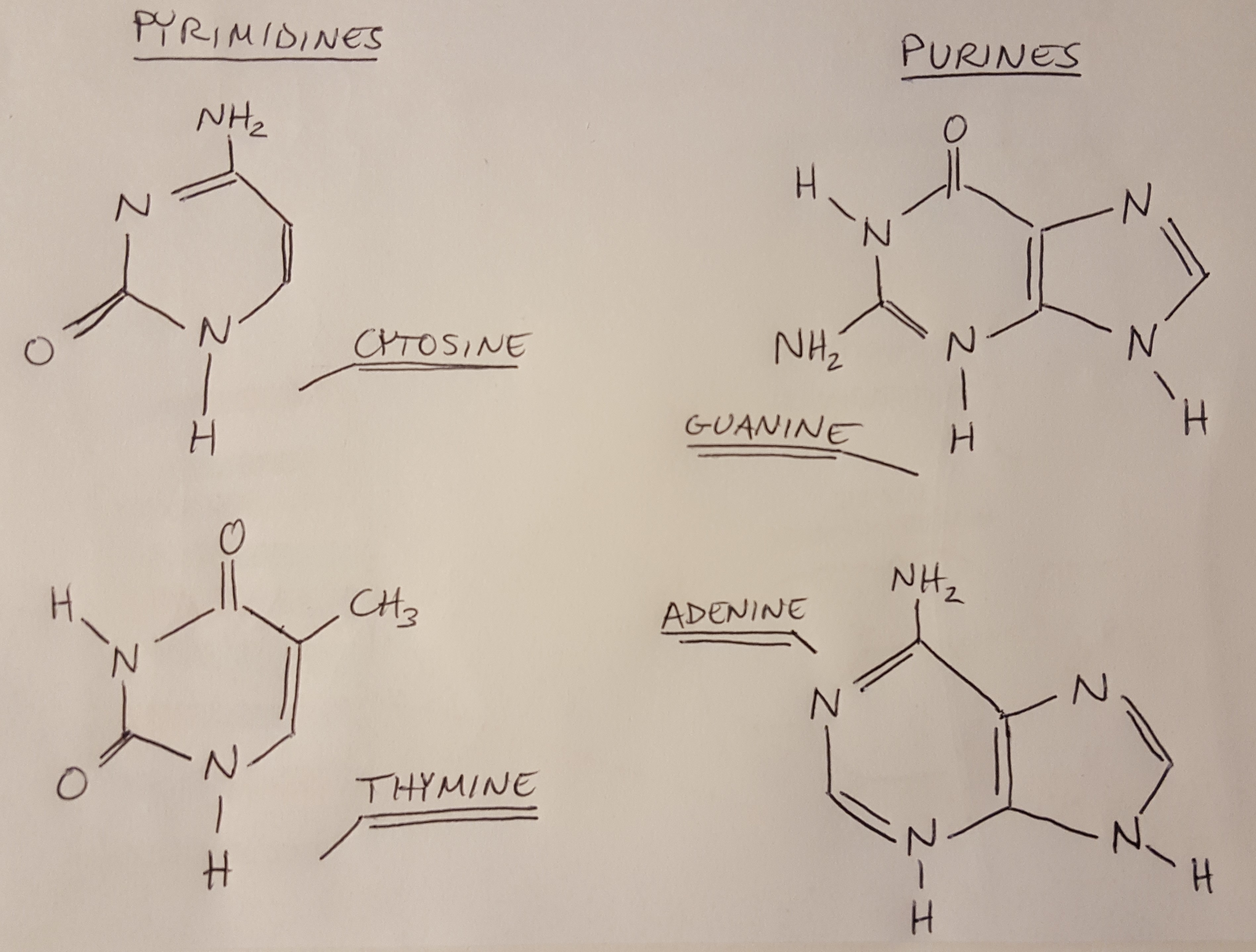
These nitrogenous bases are attached to C1 of deoxyribose through a glycosidic bond. Unlike DNA RNA contains a uracil nitrogenous base instead of thymine. Adenine and guanine are purine bases whereas cytosine and thymine are pyrimidine bases.
And more than 999 of our DNA sequence is the same. The structure of DNA was determined by American geneticist James Watson and British biophysicist Francis Crick in 1953. On average a human gene will have 1-3 bases that differ from person to person.
The various juxtapositions of these 4 bases give rise to the genetic codes of all the biota on the planet. Bases interact through weak bonds called hydrogen bonds that can be easily broken and reformed. Adenine A Thymine T Guanine G and Cytosine C.
The complimentary of the strands are due to the nature of the nitrogenous bases. To form a strand of DNA nucleotides are linked into chains with the phosphate and sugar groups alternating. DNA is organized into structures called chromosomes and housed within the nucleus of our cells.
DNA deoxyribonucleic acid is a type of macromolecule known as a nucleic acidIt is shaped like a twisted double helix and is composed of long strands of alternating sugars and phosphate groups along with nitrogenous bases adenine thymine guanine and cytosine. UAGGCUAA First think about which base pairs arise in complementary strands of DNA. The pairing of the nitrogenous bases that are connected to the sugar-phosphate backbone play a key role in the ability of DNA to store and transfer genetic information.
While DNA has the ATCG nitrogenous bases RNA replaces thymine with uracil making its bases AUCG. This is important during DNA replication where the two DNA strands must be separated before being copied and important for a cells ability to read the instructions found within the DNA. DNA structure showing the nucleotide bases cytosine C thymine T adenine A and guanine G linked to a backbone of alternating phosphate P and deoxyribose sugar S groups.
All humans have the same genes arranged in the same order. DNA DNA adenine thymine A T thymine adenine T A cytosine guanine C G guanine cytosine G C However mRNA does not consist of the same four bases as DNA. Nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine guanine cytosine and thymine.
But the few differences between us all 14 million of them are enough to make each one of us unique. All the nitrogenous bases are at the core centre of the helix. In DNA nucleotides are linked to form a chain and the order of the arrangement of nucleotides stores the genetic information of the cell.
National Library of Medicine NLM. A nitrogenous base is an organic molecule that contains the element nitrogen and acts as a base in chemical reactions. Know more about these DNA bases in this post.
The nitrogenous bases in DNA pair together A with T and C with G to form base pairs that appear as horizontal bars in DNA models. A nucleotide is composed of three distinctive chemical sub-units. Nucleotide Structure Courtesy of the National Human Genome Research Institute.
The structure of DNA is tied to its function. The nitrogenous bases that compose the deoxyribonucleotides include adenine cytosine thymine and guanine. A DNA nucleotide contains deoxyribose sugar whereas an RNA contains the sugar ribose in every nucleotide.
The DNA will not be double stranded because the double-stranded nature of DNA is due specifically to the opposite attractive nature of purine nitrogenous bases with pyrimidines. A nucleotide is the basic structural unit and building block for DNAThese building blocks are hooked together to form a chain of DNA. Adenine abbreviated as A thymine abbreviated as T guanine abbreviated as G and cytosine abbreviated as C.
The nitrogenous bases in DNA are what stores genetic information and they are also responsible for encoding phenotypes the visible traits of the genetic code. These building blocks are made of three parts. Deoxyribose attached to a.
The sugar-phosphate backbone as mentioned is an important component of DNAs double helix structure. Nucleotides in DNA are molecules made of deoxyribose sugar a phosphate and a nitrogenous base. The nitrogenous bases in DNA are of four types.
The nitrogen bases are also called nucleobases because they play a major role as building blocks of the nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid. With the general acceptance of DNA as the chemical basis of heredity in the early 1950s many scientists turned their attention to determining how the nitrogenous bases fit together to make up a threadlike molecule. Guanine and adenine are both purine bases and their structure is a six sided ring combined with a five sided structure.
Here without an opposite to pair to opposing strands of artificial DNA will not attract to. The base adenine always interacts with a thymine A-T on the opposite strand via two hydrogen bonds and cytosine always interacts with guanine C-G via three hydrogen bonds on the opposite strand. The basic property derives from the lone electron pair on the nitrogen atom.
DNA is a macromolecule consisting of two strands that twist around a common axis in a shape called a double helixThe double helix looks like a twisted ladderthe rungs of the ladder are composed of pairs of nitrogenous bases base pairs and the sides of the ladder are made up of alternating sugar molecules. Human DNA is made up of around 3 billion base pairs and more than 99 of those bases are the same in all people according to the US. A molecule of DNA consists of two strands that form a double helix structure.
The backbones of both DNA and RNA are a sugar molecule and a phosphate group. The nitrogenous bases in DNA can be adenine guanine cytosine and thymine. There are four types of nitrogenous bases.
Purines Adenine A and Guanine G and pyrimidine Cytosine C and Thymine T. Hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases allow the molecule to exhibit the double. Similar to the way the.
A five-carbon sugar molecule a nucleobasethe two of which together are called a nucleosideand one phosphate groupWith all three joined a nucleotide is also termed a nucleoside monophosphate nucleoside diphosphate or nucleoside triphosphate depending on how many phosphates make up the phosphate group. The DNA of all the living beings is composed of just four bases ie.

What Nitrogenous Bases Are Found In Dna Get The Answer At Byju S Neet
Dna
Dna Structure

Nitrogenous Bases Bioninja
Dna Structure

Nitrogenous Bases Bioninja

Structural Formulas Purine Pyrimidine Nitrogenous Bases Stock Vector Royalty Free 188742425
Nitrogenous Bases
Comments
Post a Comment