Dipole Dipole Forces
Dipole-induced dipole - a polar molecule interacting with a nonpolar one. A H2S b CH3CH3 c CH3OH d Ar 3.

Ion Dipole Forces Definition Overview Expii
What Types Of Intermolecular Forces Occur Between Two Polar Molecules Quora
What Are Dipole Dipole Forces Quora
A Hydrogen bond is a dipole-dipole interaction.

Dipole dipole forces. Dipole-dipole - Interaction of polar molecules with other polar molecules examples. Two factors determine whether a substance is a solid a liquid or a gas. This is used to determine the quantum phase diagram associated to the ground state of the system and quantify the effect of the dipole-dipole Hamiltonian interaction.
Molecular dipoles occur due to the unequal sharing of electrons between atoms in a molecule. Intermolecular Forces Complications Any molecules that experience one type of attraction also experience all the weaker types of attractions HCl molecules experience. The hydrogen bond is often described as a strong electrostatic dipoledipole interaction.
If you are also interested in hydrogen bonding there is a link at the bottom of the page. Write the following in the increasing order of boiling points. These forces are responsible for the liquids solids and solutions state of any compound.
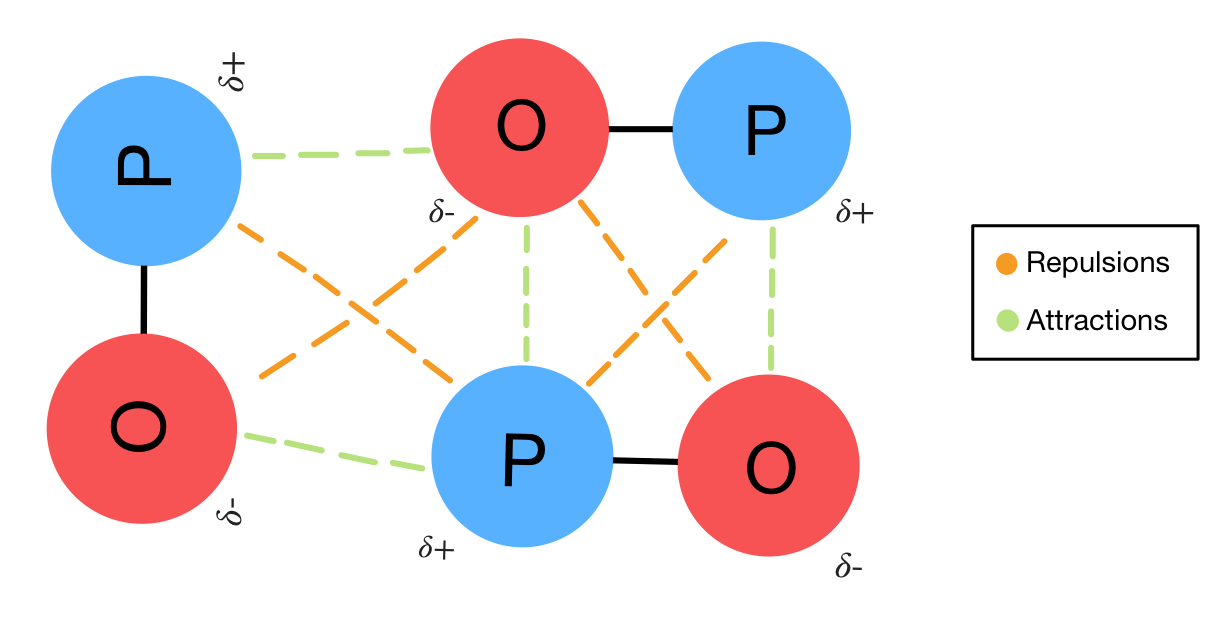
Therefore in liquid acetone for example favorable dipole-dipole interactions outweigh unfavorable dipole-dipole interactions. A dipole-dipole interaction is an attraction or repulsion between polar molecules. Although we talk as though electrons distribute their time evenly among all atoms in a molecule some.
Some common types of intermolecular forces are London dispersion dipole-dipole Hydrogen bonding and ion-ion force. N 2 or CO. In the trans isomer the dipole moment is zero because the two CCl bonds are on opposite sides of the CC and cancel and the.
Acetone in acetone triethyl amine in acetone Hydrogen bonding - special case of dipole-dipole when there is a H bonded to a N O or F. A HCl b CH3CH3 c CH3NH2 d Kr 2. By considering real induced electric dipole moments we find the quantum phase transitions for 2- and 3-level atomic systems interacting with 1- and 2- modes of the electromagnetic field respectively.
Ion-Dipole Dipole-Dipole Dispersion Forces hMgSO 4 s Ion-Ion Ion-Dipole Dipole-Dipole Dispersion Forces iHeptane C 7 H 16 l Ion-Ion Ion-Dipole Dipole-Dipole Dispersion Forces Which of the following has the highest boiling point. Dispersion forces are also considered a type of van der Waals force and are the weakest of all intermolecular forces. There are three types of intermolecular forces known as dipole-dipole forces London dispersion forces and hydrogen bonding forces.
An example in organic chemistry of the role of geometry in determining dipole moment is the cis and trans isomers of 12-dichloroetheneIn the cis isomer the two polar CCl bonds are on the same side of the CC double bond and the molecular dipole moment is 190 D. The especially strong intermolecular forces in ethanol are a result of a special class of dipole-dipole forces called hydrogen bonds. Dipole-Dipole forces exist between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule.
Polar covalent bonds behave as if the bonded atoms have localized fractional charges that are equal but opposite ie the two bonded atoms generate a dipoleIf the structure of a molecule is such that the individual bond dipoles do not cancel one another then the molecule has a net dipole moment. This term is misleading since it does not describe an actual bond. They occur whenever there is a separation of positive and negative charges.
A hydrogen bond is the attraction between a lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom of one molecule and the electron-deficient hydrogen atom of a nearby molecule. A hydrogen bond is the attraction between a hydrogen bonded to a highly electronegative atom and a lone electron pair on a fluorine. Solution CO and N 2 are both diatomic molecules with masses of about 28 amu so they experience similar London dispersion forces.
Identify the intermolecular forces in each of the following substances. The positive region of one molecule is attracted to the negative region of another and repulsed by the positive region of another molecule. Why do different liquids boil at different temperatures.
Those atoms that are more electronegative pull the bonded electrons closer to themselves. In liquids the orientations of molecular dipoles change rapidly as molecules tumble about. Dipole-dipole interactions fall off with 1r 3.
However dipole moments tend to orient favorably. This page explains the origin of the two weaker forms of intermolecular attractions - van der Waals dispersion forces and dipole-dipole attractions. Dipole-dipole forces Hydrogen bonding Ion-ion forces.
Dipoledipole forces occur between molecules with permanent dipoles ie polar molecules. Kinetic energy tends to keep the particles moving apart. For molecules of similar size and mass the strength of these forces increases with increasing polarity.
A hydrogen bond is an extreme form of dipole-dipole bonding referring to the attraction between a hydrogen atom that is bonded to an element with high electronegativity usually nitrogen oxygen or fluorine. These are called hydrogen bonds and are stronger than conventional dipole-dipole forces. They are often called London forces after Fritz London 1900-1954 who first proposed their existence in 1930.
However it also has some features of covalent bonding. Dipole-dipole forces are similar in nature but much weaker than ionic bonds. All these bonds occur due to electric charges resulting from the arrangement of electrons and nuclei in the molecules.
Definition of a Dipole. 2 carbon monoxide CO London dispersion forces 3 silicon tetrafluoride SiF 4 London dispersion forces 4 nitrogen tribromide NBr 3 dipole-dipole forces 5 water H 2 O hydrogen bonding 6 acetone CH 2 O dipole-dipole forces 7 methane CH 4 London dispersion forces 8 benzene C 6 H 6 London dispersion forces. Intermolecular attractions are attractions between one.
Polar molecules can also induce dipoles in nonpolar molecules resulting in dipoleinduced dipole forces. It is directional stronger than a van. A dipole is a molecule that has both positive and negative regions.
Londons dispersion force dipole-dipole H-bonding Ion-ion. The kinetic energies of the particles atoms molecules or ions that make up a substance. Caffeine molecules have bond dipoles that measure the polarity of a chemical bond within a molecule.
Dipole dipole forces occur between polar molecules and are due to permanent dipoles in the molecule. Again one could use Figure IVA to have students predict the boiling point for HF rather than just showing the boiling point as provided in Figure IV. Dipole-Dipole Forces and Their Effects Predict which will have the higher boiling point.
Water acetic acid acetone in water. Between CO2 and SO2 only _____ will have dipole-dipole interaction because _____. Because CO is a polar molecule it experiences dipole-dipole attractions.
Among the three types hydrogen bonds are the strongest form of intermolecular bonds. The attractive intermolecular forces between particles that tend to draw the particles together. The buildup of electron density around an atom or discreet region of a molecule can result in a molecular dipole in which one side of the molecule possesses a partially negative.
It has to do with how strongly the molecules interact with each other through intermolecular forces. Hydrogen bonding which is the strongest form of dipole-dipole interactions and. The order of strength of these intermolecular forces is given below.

Intermolecular Forces 1 Dipole Dipole Forces Youtube

Hydrogen Bonding Dipole Dipole Ion Dipole Forces Strong Intermolecular Forces Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Dipole Dipole Forces Definition And Examples
Difference Between Dipole Dipole And London Dispersion Forces Pediaa Com

Intermolecular Forces Emedicalprep
Chemistry Intermolecular Bonding

Dipole Dipole Forces Animation Intermolecular Force Chemistry Molecules
Dipole Dipole Interactions Definition Overview Expii
Comments
Post a Comment